When looking for a new laptop more often than not, the processor is the first thing you look at on the spec sheet. To be honest, Intel processor names can be confusing.
What do the Intel processor names, letters and numbers mean?
In this article, we take a look at Intel’s naming scheme and convention of two common processors found in laptops – the Intel Core I-series and Intel Xeon processors.
Here’s everything you need to know about the Intel naming scheme.
Intel Naming Scheme Explained: Intel Letters and Numbers Meaning
Understanding Intel processor names are very important. Because it tells you the computing power of the computer or laptop.
Intel Core I-series
Intel Core I-series Names
The Core I-series is the most common and popular processor found in laptops and desktops. There are the Intel Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 and Core i9.
Intel Core i3 is found in a lot of cheap and budget laptops. Because of its low processing power, it can only handle everyday tasks.
It is the best processor to get if you want something cheap and for everyday use. Its processing power can be deduced from the letter suffix.
The Core i5 is more powerful than the Core i3 and can handle tasks that require a lot of processing power. These processors are occasionally found in gaming laptops and mid-tier laptops.
The Core i7 is the next most powerful out of the Core I-series. Designed to handle heavy-duty tasks.
Core i7 processors are found in high-end laptops and are the most preferred processor when it comes to looking for a laptop for professional use.
The Core i9 is for heavy-duty applications and beyond. They have the highest clock speed out of the Core I-series and the most powerful processor.
What Do Intel Letters Mean?
Not all Core i3, i5 and i7 processors are the same. The Core I-series processors have different suffix letters that indicate their processing power. Here are what the suffix letters mean in the Core I-series processors.
The “U” stands for ultra-low power processors. They draw less power and have low clock speeds. They also do run at high temperatures.
U processors are commonly found in a lot of laptops especially laptops that are slim and lightweight.
Because of the slim and thin factor and the tendency not to produce a lot of heat U processors are commonly found in them.
The “H” comes in three versions – H, HK and HQ. Both are powerful processors that consume a lot of power and have high clock speeds. They also tend to run hot when a lot of processing power is needed.
The H processors are quad-core or Hexa-core. Core i5 processors with H suffix are quad-core whilst the Core i7 are Hexa-core. Laptops that have HK are unlocked.
Unlocked in the sense that it can be overclocked. The HQ suffix indicates a high-performance quad-core processor. Anytime you see a Core I-series that ends with H, HK, or HQ. It is a high-performance processor that can be overclocked.
The “G” stands for high-performance processors. They consume a lot of power, run hot and have high clock speeds.
What makes them different is that they have powerful discrete graphics cards that are from AMD. To be precise AMD Radeon Vega graphics card.
H processors normally come with discrete NVIDIA graphic cards. That’s what makes the G different.
The “Y” stands for very ultra-low processors even lower than the U. It is a power-efficient processor and doesn’t overheat. Laptops that are super slim and thin have Y processors.
The “T” stands for power-efficient processors. T processors consume a lot of power and have high clock speeds compared to U processors. They lie somewhere between U and H. They are also uncommon. Few laptops have T Processors.
The “K” supports overclocking.
The “F” stands for no integrated graphics card.
The “M” processors stand for mobile processors. These processors are commonly found in the older Lenovo ThinkPads. When M processors are quad-core it becomes MQ.
The “X” denotes the powerful processors. It is either X or XE where the E stands for extreme. These processors are needed when you plan to go balls to the wall in terms of computing power.
Gaming, virtual reality, music production, 4K and 360-degree video editing. You name it. Anything that requires a lot of processing power and cores. Intel Core processors that have the letter suffix X will be able to handle it. They are also the most expensive.
Intel Core Processor Number Meanings
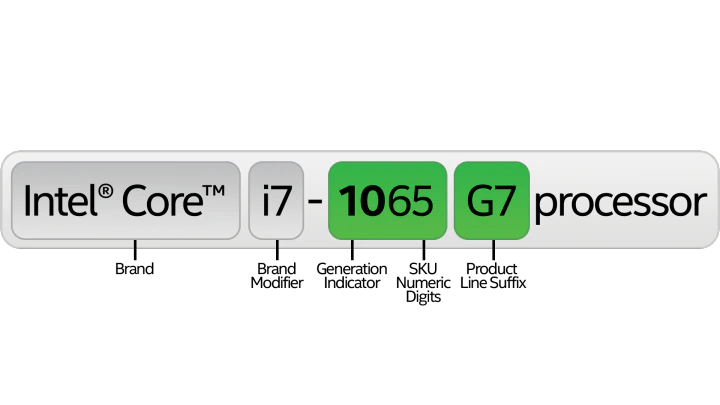
Every Intel Processor has numbers. The three numbers before the suffix letter are the Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) numeric digits and also provide information on the processing power.
For example, an 8th Gen Intel Core i5-8350U – where 350 is the SKU numeric digits – is more powerful than an 8th Gen Intel Core i5-8250U by eight per cent according to Userbenchmark.
Same applies to an 8th Gen Intel Core i7-8750H and 8th Gen Intel Core i7-8850H. This comparison only works when you compare two processors that are in the same generation and have the same processor name.
Intel Core Processor Generations
Intel Core processor generations are a good way to quickly determine how good a processor is. The latest Intel generation processors are always going to be faster and better than previous generations.
According to Userbenchmark, the 8th Gen i7-8550U is a whopping 22 per cent faster than its previous 7th Gen i7-7500U.
In shopping for a new laptop always go for the latest generation. But how do you find the generation of the Intel processor?
Some spec sheets are kind enough to tell you what generation the processor is others not so much. If it isn’t indicated the first number always tells you what generation the Intel processor is.
For example, an i7-7500U processor is a 7th Generation processor. The 7 in the 7500U means it is 7th Generation.
So if you have an i5-11300H, the 11 in 11300H indicates that it is a high-performance 11th Generation processor.
How To Check Your Intel Processor Generation On Your Laptop
Here’s how to check what generation your processor is in your laptop.
For Windows
Hit the Windows + R buttons.
Enter dxdiag into RUN and click OPEN.
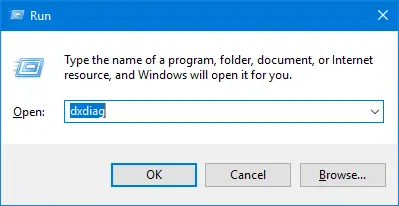
A dxdiag dialog box will open. Under the SYSTEM tab look for the processor. You will then see what processor and generation your laptop has. Mine is an Intel Core i5-5200U processor where 5 in the 5200U indicates that it is a 5th Generation processor.
Intel Xeon Processors Explained
Intel Xeon processors are processors that do not cater to the consumer market but rather are optimized for 3D modelling, rendering, CAD works and high-performance tasks.
They are designed to withstand long hours of heavy loads without experiencing throttling.
Intel Xeon Processor Names Meaning
Intel Xeon processor names take a slightly different approach than the Intel Core processors. Whiles Intel Core I-series have i3, i5 and i7. Intel Xeon goes with E, E3, E5 and E7.
Intel Xeon E processors are either quad-core or hexa-core.
Intel Xeon E3 processors are quad-core processors.
Intel Xeon E5 processors range from quad-core to have 22 cores.
Intel Xeon E7 processor range from octa-core to 24 cores.
All Intel Xeon processors have high clock speeds to be able to handle intensive tasks for long periods of times.
Intel Xeon Processor Letter Meanings
Intel Xeon also has their own suffix of letters differentiating them from one another in the same family.
The “L” stands for low-power. These Xeon processors consume less power and have low clock speeds amongst Xeon processors.
The “W” stands for workstation processor. They are high-performance Xeon processors with high clock speeds. These are only used in enterprises and are found in workstation desktops.
The “M” stands for mobile. Xeon processors with M suffix are found in mobile workstations. Their performance lies between the L and W Xeon processors.
Intel Xeon Processor Number Meanings
Let’s take the Xeon processor Intel Xeon E-2176M. The four digits 2176 represents the product family. The 2 in 2176 is the maximum number of CPUs in a node. The 1 in 2176 represents the socket type.
The last two numbers 76 are the processor’s Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) numbers. Most spec sheets include a V2, V3 etc. at the end.
The V indicates the version is something similar to the generation in Intel Core I-series CPUs.
Final Thoughts
Now that we have covered the common Intel processors seen you won’t have any problems understanding their names, numbers and letters.
You can also easily tell which generation it is and decide if a laptop is worth purchasing. That’s everything about Intel’s CPU naming scheme.
