Windows registry is a database repository that stores the settings and configurations for everything on a Windows PC – user passwords, windows settings, applications etc.
The initial settings for everything on the Windows PC are stored as keys and subkeys.
It acts as a single place to store all the settings and configurations of applications found on Windows. It is also a hierarchical database. Here’s everything you need to know in understanding Windows Registry.
What is Windows Registry (Regedit) used for?
Because the windows registry is a database repository. Anytime you install a new program, the information, settings and configuration about the program are added to the registry.
This information can be accessed by you, the user, or other programs on Windows.
The windows registry is also used to modify or create new registry entries or keys.
An example is increasing the amount of video ram on an integrated graphics card. You can do this by creating and modifying keys.
In short, the windows registry is used for collecting and storing settings of all applications found on Windows that can be modified or used as a reference by other applications or by the user.
How to Open Windows Registry
Opening the windows registry is very simple. Here’s how to do it.
Method 1

- Press the Windows key and enter regedit.exe.
- Click it and Windows registry will open
Method 2
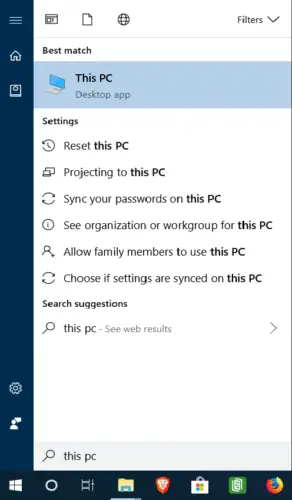
- Press the Windows key.
- Type This PC.
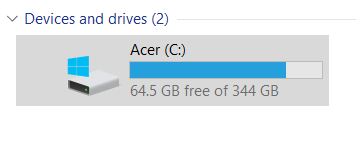
- Go to your C: drive or main drive.
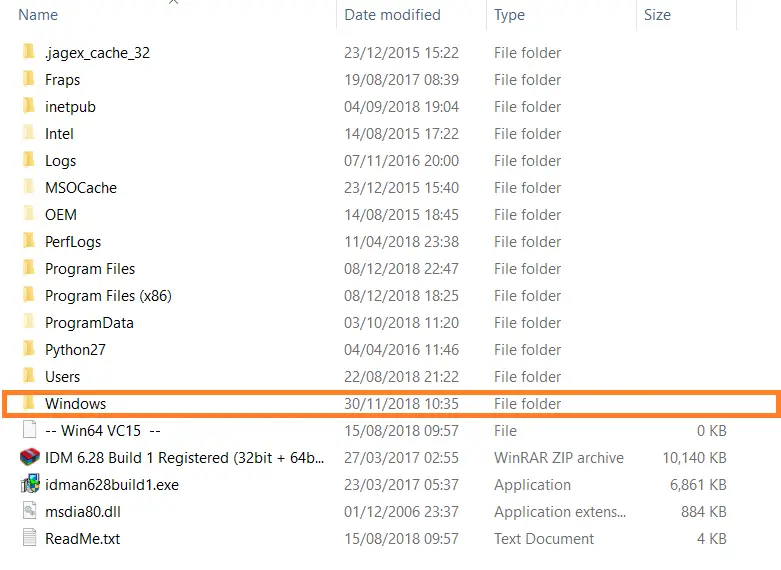
- Open the Windows folder.
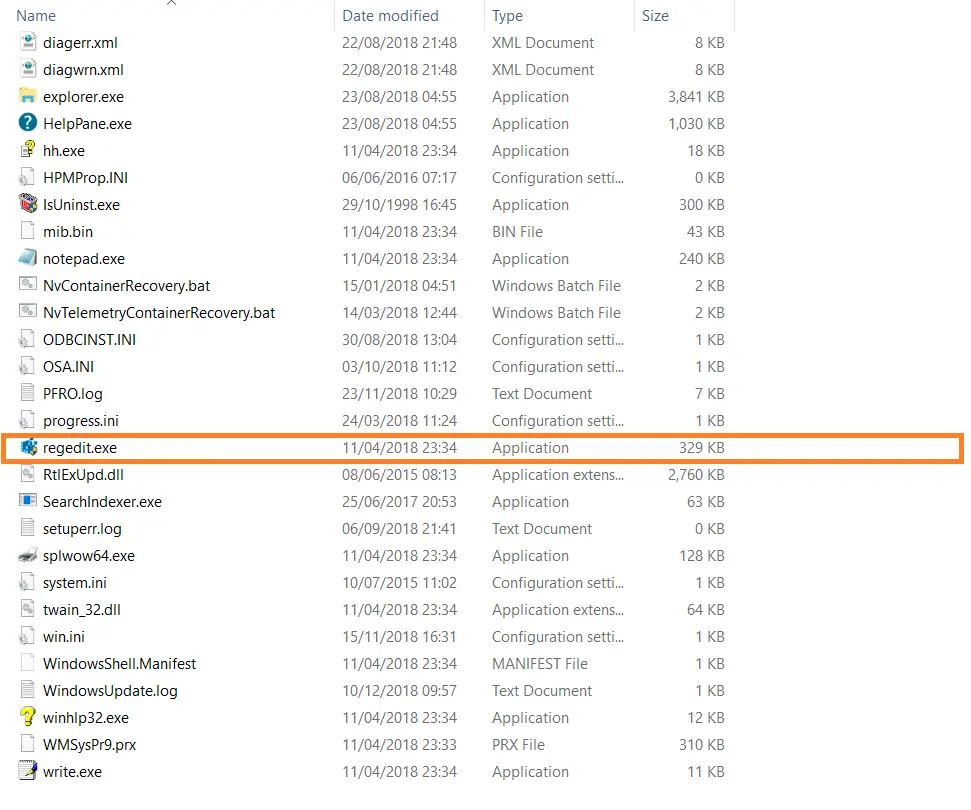
- Look for Regedit.exe and open it as administrator.
Method 3
- Press Windows key + R.
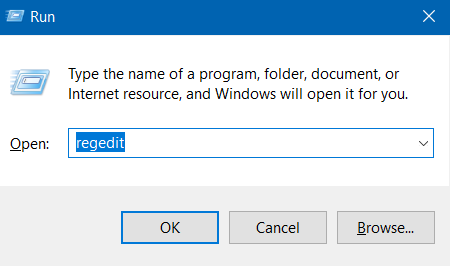
- Type in regedit and click OK
Method 4
- Open command prompt

- Make sure you are in C:\User\Username>

- Type in regedit and hit enter.
Understanding The Windows Registry

Before using the windows registry you have to understand it. The windows registry is a hierarchical database.
Every major folder having its subfolders which also have their folders with a key in them. There are five major folders in the windows registry.
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT

The HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR) key contains file name extension associations and COM class registration information.
This deals with the software settings above the file system, shortcut information, information on file associations and other user interface are stored in this hive.
It contains the necessary information to know what to do when you want it to do something.
It contains the necessary information to know what to do when you want it to do something.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU)

The HKCU key contains the settings of the user logged on. Any information such as the login names, start menu settings, desktop background etc.
Everything concerning the user that has currently logged in is stored in this key. Any change that occurs in the key only affects the current user.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM)

The HKLM stores specific information or configuration settings about the software, hardware, security, and other preferences on a given PC for all users to have access to.
HKEY_USER (HKU)
This key has information on the user’s folders, choices of themes, colours and Control Panel settings made by the user.
- How To Remove/Disable Cortana in Windows 10
Basically, anything that concerns the user or user profile is stored here. Each user profile has their own subkey for storing their user profile.
This basically where individual preferences are stored in a PC that has numerous user profiles.
HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG (HKCC)

The HKCC key stores the current hardware settings which point to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE.
A shortcut to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE that keeps information about the hard profile.
You can make changes in the HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG which will also take effect in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE.
Other Information Concerning The Windows Registry
Keys in the windows registry are stored as one of the five data types:
String Value
Stored as a string that is, words or letters that is easily read by humans
Binary Value
Keys are stored as raw binary data and can be displayed as in hexadecimal format. Hardware component information is stored as binary data.
DWORD (32-bit) Value and DWORD (64-bit) Value
Keys stored in this format are expressed as either decimal or hexadecimal format. The 32-bit and 64-bit refer to the bit length of the value.
Multi-string Value
Multi-string values contain lists or multiple values as opposed to the string value where it can just contain one value.
Expandable String Value
An expandable string value is just like a string value but contains variables.
When Windows call upon these types of strings their values are expanded out to what the variable defines hence the name expandable string value.
Backing-up the Windows Registry
If you like to configure or tweak Windows you can do so through the windows registry, but be warned.
Although you can use windows registry to inspect and modify the data found there incorrect changes made to the windows registry can seriously mess up your PC.
Make sure you know what you doing or follow an expert’s advice before you decide on making those changes. Regedit has no undone if you screw up.
Also, back-up your data or create a system restore point so that if anything happens you will be able to solve it easily.
Here’s how to do a backup
- Open Regedit.
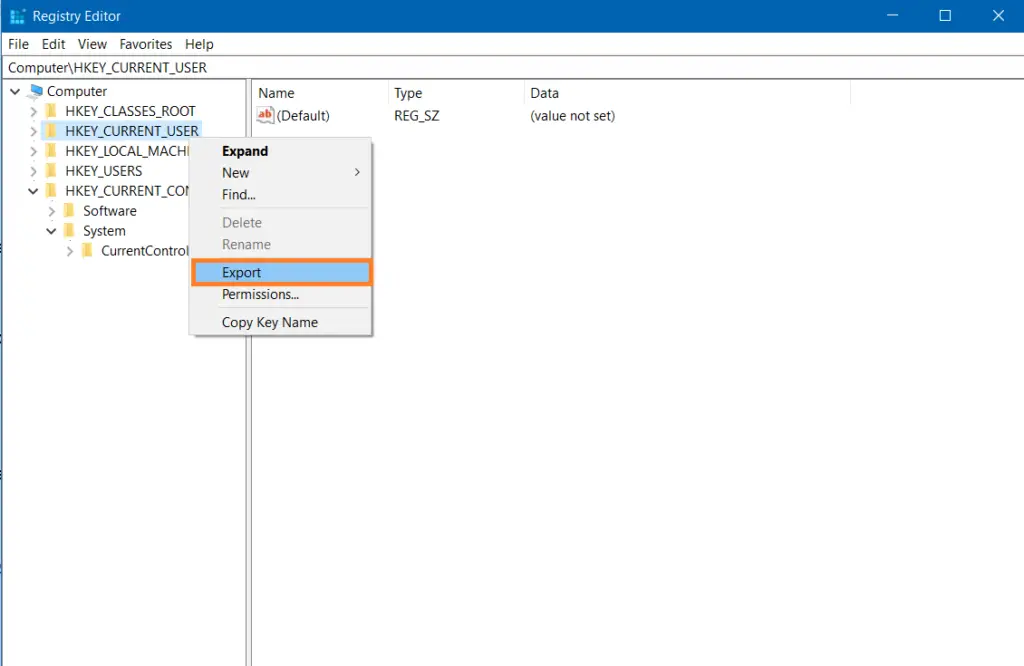
- Right-click the folder (key) you want to back up and select Export.
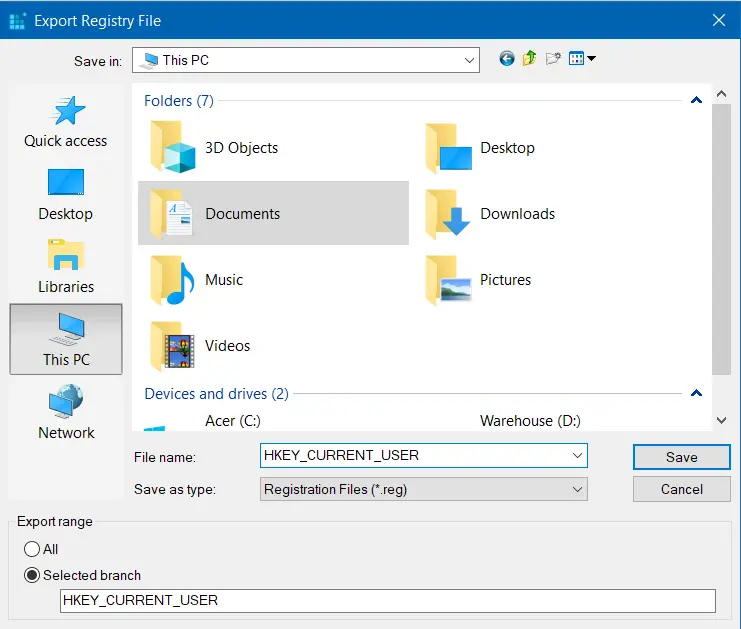
- A dialogue box will open. You save anywhere you want to. Make sure you name the file as the original.
- Restoring the Registry Key
- Open Regedit

- Click on the file in the menu bar and choose import.
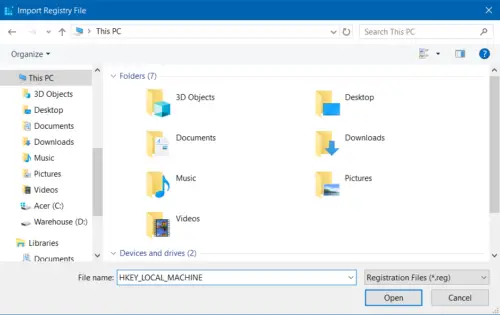
- A dialogue box will open. Select the registry key or folder you want to restore.
There easiest and most foolproof way is to create a system restore point. This is a point where your system can go back to if you messed up in the registry.
How To Edit The Windows Registry

You know what the windows registry is, you understand it and know how to do a back-up. This is where the geeky tech stuff starts to happen.
First of all, in editing the registry you must know what you want to edit. In the windows registry dialogue box, on the left side are the major folders (major keys or hive) which expanded will show their keys and subkeys.
On the right side are the values of the keys which you can create a new value, modify it or delete.
As an example of how to edit the windows registry, I am going to show you how to increase your dedicated video RAM.
In editing the windows registry make sure you back-up your data and consult expert guides before doing so.
Problems That Occur In the Windows Registry
The more applications you install the larger the amount of data in the registry gets. Also, uninstalling programs leaves unwanted and incorrect data in the registry accumulating as junk data.
Alteration of programs frequently, browsing websites, altering hardware etc.
The older the windows PC the more junk and useless data the registry will contain because of the fact that over the years there have been installation and uninstalling of software and the like.
Over time this causes in a reduction in system performance. Everything starts to slow down because of the junk in the registry.
Applications take longer to load boot up starts to slow down or even a system crash might happen.
The registry takes a long time to fulfil a request made by active applications and hardware causing system freezes and rebooting.
There is also the possibility of an application terminating unexpectedly due to the large size of the data in the registry.
Cleaning The Windows Registry
Back in the days cleaning the windows registry was the rave. Now, is quite rare to see a laptop with a registry cleaner.
Back then storage drives were slow and had small space compared to what we have now, super-fast solid state drives that can boot up your laptop in less than five seconds and hard disk drives that have massive storage spaces of 2 TB or 3 TB.
Will you worry about cleaning your registry very often if you had storage devices like that? I guess not.
That is not to say registry cleaners are entirely useless. You can use it to get rid of large amounts of junk data that has been accumulated.
This gives some breathing space for your laptop. It also gets rid of the unwanted cache in applications especially browsers (browsers can have large amounts of a cache of up to 2 GB or more).
Cleaning the registry does have some benefits to it but it is not entirely necessary because of the technology of storage devices.
Final Thoughts
That is everything you need to know about the windows registry, why it is important and how you can tweak it to your taste, make sure you back-up your data before doing so.

2 thoughts on “Understanding Windows Registry, What Does Regedit Do?”
Comments are closed.